In the world of online commerce, understanding the nuances of online payment processing is crucial for business success. This article delves into the key differences between a Payment Gateway and a Merchant Account, two essential components for accepting online payments. Choosing the right solution can significantly impact your business’s efficiency, security, and bottom line. We will explore the functionalities of each, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages to help you make an informed decision tailored to your specific business needs. Whether you’re a small startup or a large enterprise, understanding these core components of online payment processing is paramount for optimizing your revenue streams and providing a seamless customer experience.
Many businesses new to e-commerce are often confused by the distinction between a Payment Gateway and a Merchant Account. While they work together seamlessly, they serve distinct purposes. A Merchant Account is a specialized bank account that allows your business to accept credit and debit card payments, while a Payment Gateway acts as the bridge between your online store and the payment processor. This article will clarify these distinctions, examining the various factors to consider when selecting the right combination of Payment Gateway and Merchant Account solutions. We’ll cover key considerations such as transaction fees, security measures, integration options, and the overall impact on customer experience, empowering you to make the best choice for your business.
What is a Payment Gateway?
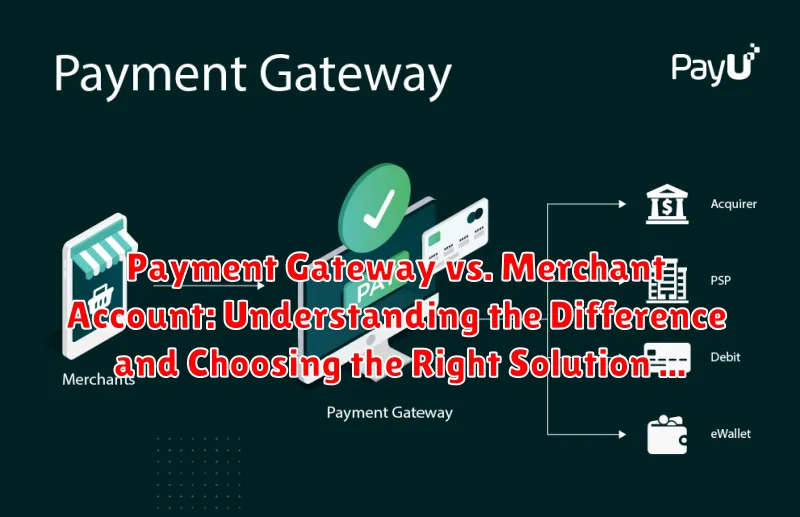
A payment gateway is a technology that acts as a bridge between your online store and the payment processor. Think of it as the virtual equivalent of a physical point-of-sale terminal you see in brick-and-mortar stores. It securely authorizes payments from customers purchasing goods or services online.
When a customer enters their payment information on your website, the payment gateway encrypts that data and transmits it securely to the payment processor. This protects sensitive information like credit card numbers. The payment gateway then receives the authorization or decline message from the processor and relays that information back to your website, completing the transaction process.
Key functions of a payment gateway include:
- Encryption of payment data
- Authorization requests to payment processors
- Settlement of funds into your merchant account
- Fraud prevention tools
Choosing the right payment gateway is crucial for ensuring smooth and secure transactions for your business.
How Does a Payment Gateway Work?
A payment gateway acts as a bridge between your customer, your online store, and the payment processor. Think of it as the digital equivalent of a physical point-of-sale terminal.
When a customer makes a purchase, the payment gateway securely captures their payment information. This information is then encrypted and transmitted to the payment processor for authorization.
The payment processor communicates with the customer’s bank to verify the funds. Once approved, the processor sends a confirmation back to the payment gateway, which then relays it to your online store. This entire process typically happens within seconds.
Key steps in the process include:
- Customer enters payment details: On your website’s checkout page.
- Encryption and transmission: The gateway encrypts sensitive data.
- Authorization request: Sent to the payment processor.
- Funds verification: The processor checks with the customer’s bank.
- Authorization response: Communicated back to the gateway.
- Transaction completion: The gateway confirms the payment with your store.
What is a Merchant Account?
A merchant account is a type of bank account that allows businesses to accept payments via credit and debit cards. It acts as a holding place for funds collected from customer card transactions before they are transferred to your business’s primary bank account. Think of it as a specialized account specifically designed for processing card-based payments.
Obtaining a merchant account involves an application process with a merchant acquiring bank. This bank assesses your business’s risk profile, industry, and processing volume. The approval process ensures that your business meets certain security standards and can handle the financial responsibilities associated with card processing.
Essentially, a merchant account is a crucial component for businesses that want to accept credit and debit card payments, providing a secure and regulated pathway for handling these transactions.
How Does a Merchant Account Work?
A merchant account acts as a dedicated holding area for customer payments before they are transferred to your business bank account. Think of it as a temporary escrow account specifically for processing credit and debit card transactions.
When a customer makes a purchase, the payment information is transmitted from the payment gateway to the acquiring bank. The acquiring bank then requests authorization from the customer’s issuing bank (the bank that issued their credit or debit card).
Once authorized, the funds are held in your merchant account. The acquiring bank then settles the transaction, typically within 1-2 business days, by transferring the funds from your merchant account to your business bank account, minus any processing fees.
Key players in this process include the merchant (you), the customer, the payment gateway, the acquiring bank, and the issuing bank. The merchant account facilitates a secure and regulated environment for these transactions to occur.
Payment Gateway vs. Merchant Account: Key Differences

While both payment gateways and merchant accounts are essential for online businesses to accept payments, they serve distinct roles. A payment gateway is the online equivalent of a point-of-sale terminal, securely authorizing and processing transactions. A merchant account, on the other hand, is a specialized bank account that receives the processed funds.
| Feature | Payment Gateway | Merchant Account |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Processes transactions | Receives funds |
| Analogy | POS terminal | Business bank account |
| Necessity | Required for online payments | Required for accepting card payments |
| Visibility | Customer-facing | Behind-the-scenes |
Choosing the Right Payment Solution for Your Business
Selecting the right payment solution is crucial for your business’s success. Factors such as business size, transaction volume, and budget play a significant role in determining the most suitable option.
For small businesses with lower transaction volumes, a payment gateway solution might suffice. These solutions offer a simplified setup and often involve lower upfront costs. However, transaction fees might be slightly higher compared to merchant accounts.
Larger businesses processing a high volume of transactions may benefit from the lower transaction fees associated with a merchant account. Although the setup process may be more complex and require more initial investment, the long-term cost savings can be substantial.
Budget is another critical factor. While merchant accounts often involve monthly fees and setup costs, the lower per-transaction fees can be advantageous for high-volume businesses. Payment gateways generally have lower setup costs, making them more accessible for smaller businesses.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific business needs. Carefully evaluate your transaction volume, budget, and technical capabilities to determine the optimal payment solution.
Benefits of Using a Payment Gateway
Payment gateways offer numerous advantages for businesses accepting online payments. They streamline the transaction process, making it easier for customers to purchase goods and services. This improved checkout experience can lead to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
Security is a major benefit. Payment gateways encrypt sensitive customer data, protecting it from fraud and unauthorized access. This builds trust with customers and reduces the risk of financial losses for your business.
Payment gateways often support a wide range of payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, and sometimes even digital wallets. This flexibility caters to a broader customer base and can increase conversion rates.
Automated transactions reduce manual processing, saving time and resources. This efficiency allows businesses to focus on other important tasks, such as customer service and marketing.
Benefits of Having a Merchant Account
A merchant account offers several advantages for businesses processing payments. Direct payment processing allows you to accept credit and debit card payments without relying on third-party processors, often resulting in lower transaction fees compared to payment gateway-only solutions. This can significantly impact profitability, especially for high-volume businesses.
Increased control over your funds is another key benefit. Money goes directly into your bank account, giving you quicker access and greater flexibility in managing your finances.
Having a merchant account can also enhance your business credibility. It projects a more professional image to customers, boosting their trust and confidence in your business operations.
Finally, merchant accounts often offer advanced security features and fraud protection tools to safeguard your business and customers from potential risks.
Integrating Payment Gateways with Your E-commerce Platform

Integrating a payment gateway with your e-commerce platform streamlines the checkout process for your customers. Most platforms offer pre-built integrations with popular payment gateways, simplifying the setup process significantly. This typically involves installing a plugin or extension and configuring your account credentials.
When choosing a payment gateway, consider its compatibility with your specific e-commerce platform. Check for existing integrations or available APIs that allow for seamless communication between the two systems. A smooth integration ensures a positive customer experience by minimizing technical glitches and ensuring secure transactions.
Some platforms offer built-in payment solutions. While these can be convenient, they may have limitations in terms of customization and features compared to dedicated payment gateways. Evaluate your business needs and choose the integration method that offers the best balance of ease of use and functionality.
Testing the integration thoroughly before going live is crucial. This includes testing various transaction scenarios, including successful payments, refunds, and declined transactions. A robust testing process helps identify and resolve any issues before they impact your customers.